
11 Sustainable Cities and Communities (162)
Make cities and human settlements inclusive, safe, resilient and sustainable
UT joins forces with two state agencies to promote healthy forests and their wildlife in Tennessee
Written by Katie Donaldson One of the goals behind a recent partnership among UTIA and state agencies is the promotion of heartier food species such as this oak. The new five-year agreement between the UTIA Tree Improvement Program, the Tennessee Division of Forestry and the Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency focuses on developing locally adapted and genetically improved seed for future Tennessee forests. Allison Mains/UTIA
One of the goals behind a recent partnership among UTIA and state agencies is the promotion of heartier food species such as this oak. The new five-year agreement between the UTIA Tree Improvement Program, the Tennessee Division of Forestry and the Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency focuses on developing locally adapted and genetically improved seed for future Tennessee forests. Allison Mains/UTIA
UTIA Tree Improvement Program and state agencies work together to protect and conserve the state’s forest resources
Katie Donaldson is a communications specialist for the University of Tennessee School of Natural Resources.
KNOXVILLE — A new, five-year agreement establishes how the state of Tennessee and a program in the University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture will study and produce tree seedlings to promote the protection and conservation of Tennessee forests.
The UTIA Tree Improvement Program (UT-TIP), the Tennessee Department of Agriculture Division of Forestry (TDF) and the Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency (TWRA) partnered on the agreement.
“Honoring our land-grant mission, we are excited about this partnership to responsibly research, develop, manage and conserve forest resources across the great state of Tennessee,” said Keith Carver, UTIA senior vice chancellor and senior vice president.
UT-TIP manages numerous seed orchards in East, Middle and West Tennessee with help from state and federal partners. It uses the orchards to provide the East Tennessee Nursery with locally adapted and genetically improved seed.
Editorial: Despite the rhetoric, responsible growth is a bipartisan goal
Written by Coffee County for Responsible Growth
Coffee County is under development pressure, but it’s not a political fight
This editorial was provided by Coffee County for Responsible Growth, but applies to planning and development debates throughout the Southeast.
MANCHESTER — We keep hearing the claim that land protection, conservation and zoning are “liberal issues.”
Let’s set the record straight: That’s simply not true.
Protecting Coffee County’s farmland, water, infrastructure and rural way of life isn’t a political talking point — it’s common sense. And it’s deeply bipartisan.
We’ve got Conservatives, Republicans, Democrats, Independents and Libertarians all standing together. Not because of party lines — but because we love where we live, we recognize the importance of agriculture, and we value community.
Play Knoxville: Put an idea pin in public recreation assets, greenways and parks
Written by City of Knoxville Those with ideas they want to contribute to the Knoxville Parks and Rec master plan can do so by way of an interactive map. Shown here are many of the center city’s public recreation assets. Note the size of the Urban Wilderness, a valuable natural and recreational resource accessible to the visitors and the city’s 200,000 residents. Hellbender Press
Those with ideas they want to contribute to the Knoxville Parks and Rec master plan can do so by way of an interactive map. Shown here are many of the center city’s public recreation assets. Note the size of the Urban Wilderness, a valuable natural and recreational resource accessible to the visitors and the city’s 200,000 residents. Hellbender Press
The city invites the public to share input on the future of Knoxville parks, including greenways and the urban wilderness; citizens can put a pin in a park with their ideas
KNOXVILLE — The public engagement phase for Play Knoxville, the City’s Parks & Recreation Master Plan, is now underway. The master plan will help guide investments in parks, greenways, community centers and programming over the next decade.
The planning process started in January with the formation of a steering committee of community leaders. Since then, city staff and consultants from Perez Planning + Design have conducted dozens of focus groups, one-on-one meetings with City Council and cabinet members, and site visits to nearly 70 parks across Knoxville.
Over the coming weeks, community members will have multiple opportunities to provide input through neighborhood and community meetings; public events; direct outreach and social media engagement; an interactive mapping tool and an online survey.
The Play Knoxville website is now live.
- knoxville parks master plan
- get involved in city government
- knoxville city government
- knoxville greenways
- park planning in knoxville
- perez planning + design
- play knoxville
- knoxville citizen engagement environment
- does knoxville have nice parks
- urban wilderness
- urban wilderness gateway park
- urban wilderness knoxville
Get down and dirty with history at Big South Fork celebration of spring
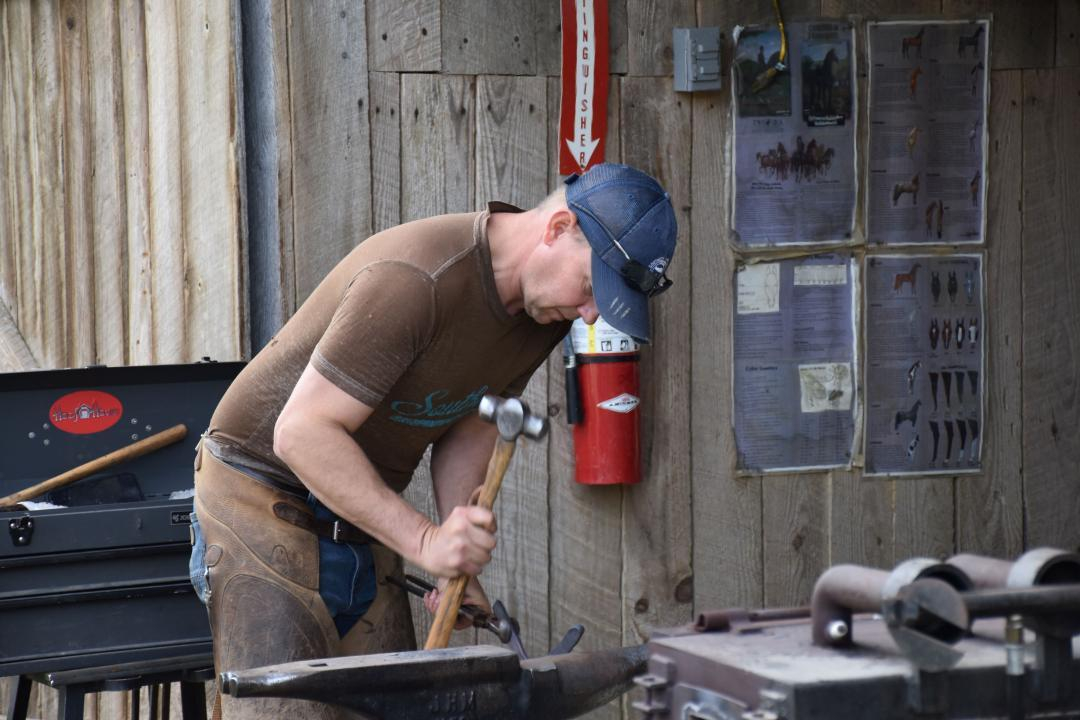 A farrier demonstrates his skills during a past installment of the annual Spring Planting and Music Festival at Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area, set this year for April 26. National Park Service
A farrier demonstrates his skills during a past installment of the annual Spring Planting and Music Festival at Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area, set this year for April 26. National Park Service
ONEIDA — Step back in time and experience history in motion at the 25th Annual Spring Planting and Music Festival from 9 a.m.-4 p.m. April 26 at Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area.
Traditions of early Appalachian settlers come to life at this free, family-friendly event. Visitors are invited to immerse themselves in the heritage of the Big South Fork region with live demonstrations, traditional crafts, music and hands-on activities that showcase the self-sufficient way of life practiced by generations past.
Set against the picturesque backdrop of the Oscar and Lora Blevins farm sites and the Bandy Creek area, the festival offers a rare opportunity to experience traditional Appalachian life. Visitors will see a variety of demonstrations and hands-on activities that highlight the skills and craftsmanship of early settlers.
One of the festival’s most anticipated highlights is the plowing and planting demonstration with mule and horse teams at the Lora Blevins field.
Children and adults alike will enjoy exploring old-time toys and taking part in interactive exhibits that make history come alive. Live music will be provided by some of the region’s most talented musicians.
Southeastern electric vehicle sales and investments arc against headwinds
Written by Stan Cross
Georgia and North Carolina lead EV investment and jobs; Florida tops market share and growth; Tennessee and Alabama lag behind
Stan Cross leads the Southern Alliance for Clean Energy dynamic Electric Transportation Team.
KNOXVILLE — Misinformation about the technology and the state of the electric-vehicle market is rampant. But beyond the noise are the facts, which show that the Southeast’s EV market is zipping along.
The Southeast continues to lead the nation in electric vehicles and battery-related jobs and private-sector investments. As of the end of 2024, updated data from the fifth annual Transportation Electrification in the Southeast report found that the region is home to a whopping 38 percent of the nation’s $215 billion in announced private-sector EV and battery investments and 31 percent of the anticipated 238,000 jobs. Georgia remains No. 1 in anticipated jobs and committed investments, with North Carolina a close second.

These investments deliver economic development and employment to our region’s rural communities. Toyota’s $13.9 billion battery manufacturing facility in Randolph County, North Carolina, is at the top of the rural economic development list. The facility is expected to create 5,100 jobs and is the nation’s most valuable clean energy investment. Hyundai has made the second-largest regional investment at its battery manufacturing and EV assembly plant in Bryan County, Georgia. That investment tops $6 billion and is expected to create 3,400 jobs. It has had a massive ripple effect, with Hyundai suppliers announcing more than $2.7 billion in investments and an anticipated 6,900 jobs across the state.
‘A day of hope:’ Months after rescue from drought, endangered laurel dace return to the wild
Written by Casey Phillips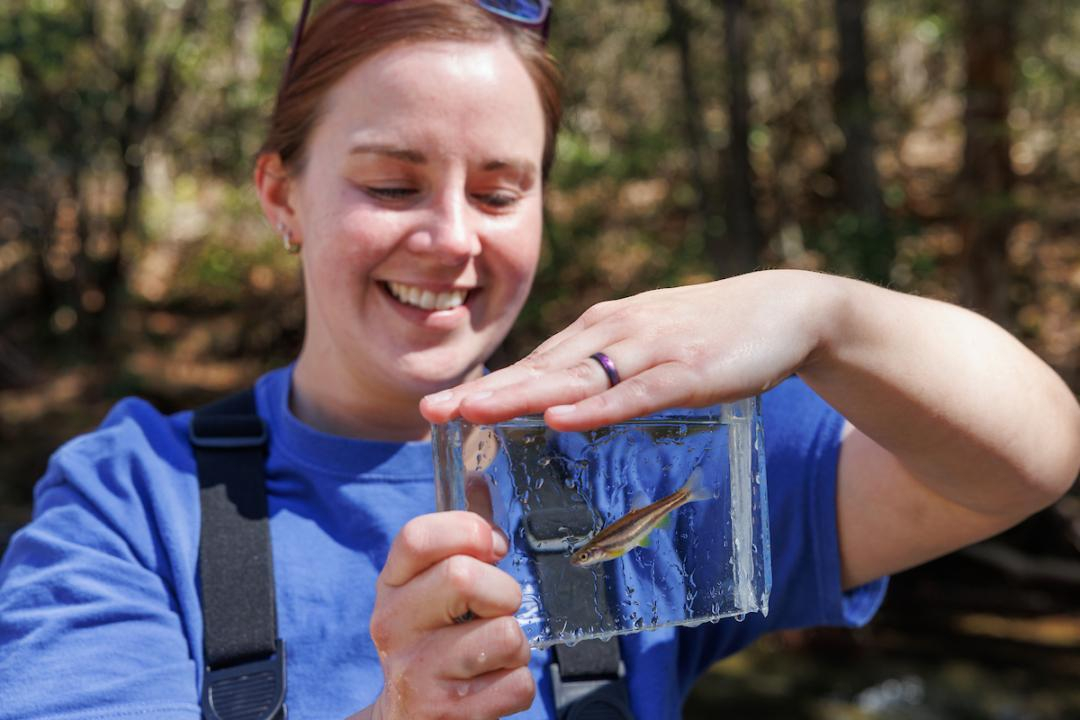 Tennessee Aquarium Reintroduction Biologist II Teresa Israel examines a critically endangered laurel dace before its reintroduction to the wild in March 2025. In July 2024, about 300 of these fish — considered by scientists to be among the most imperiled in North America — were rescued out of rapidly drying streams on Walden Ridge north of Chattanooga. Tennessee Aquarium
Tennessee Aquarium Reintroduction Biologist II Teresa Israel examines a critically endangered laurel dace before its reintroduction to the wild in March 2025. In July 2024, about 300 of these fish — considered by scientists to be among the most imperiled in North America — were rescued out of rapidly drying streams on Walden Ridge north of Chattanooga. Tennessee Aquarium
Improving drought conditions on Cumberland Plateau enabled return of fish after 2024 rescue
Casey Phillips is a communications specialist at the Tennessee Aquarium in Chattanooga.
CHATTANOOGA — After being saved from near-certain extinction last summer and overwintering in the expert care of biologists at the Tennessee Aquarium, more than 230 critically endangered laurel dace are finally back where they belong.
Last July, a prolonged regional drought caused many Southeast Tennessee streams to dwindle and, in some cases, dry up entirely. Atop Walden Ridge north of Chattanooga, water flow ceased at Bumbee Creek and Youngs Creek, the last sites known to support populations of Chrosomus saylori, the laurel dace.
When conditions in these rapidly disappearing waterways reached a tipping point, the Aquarium led a series of emergency rescue operations to save as many of these red-bellied, highlighter-yellow-finned minnows as possible. In coordination with the Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency and with assistance from the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service and the University of Georgia, about 300 laurel dace — the majority left on the planet — were relocated into the safety of human care at the Tennessee Aquarium in Chattanooga and Wolf Creek National Fish Hatchery in Jamestown, Kentucky.
According to the most recent report from the USDA’s U.S. Drought Monitor, much of Southeast Tennessee is still experiencing moderate drought conditions. However, a slightly wetter-than-average February made it safe to return these rescued minnows to the wild.
- tennessee aquarium
- laurel dace
- endangered fish
- endangered fish in tennessee
- cumberland plateau drought
- saving fish from drought
- jason miller
- anna george
- biologist ii teresa israel
- spring city, tn
- laurel dace day spring city
- chrosomus saylori
- tennesse wildlife resources agency
- twra
- us fish and wildlife service
First UT sustainability symposium offers a collaborative vision for the future
Written by Lucas Hunter
All great scientific solutions start with collaboration
KNOXVILLE — The challenges facing the planet and its inhabitants have long been too complex for any one individual or group to address, and that’s why the great advancements in modern science begin with conferences, symposiums and collaboration.
The first Environmental Future Symposium is an effort from the University of Tennessee Office of Sustainability to present a vision of the future for area residents and University of Tennessee students.
Planned for the Agriculture and Natural Resources Ballroom and Plaza from 2 p.m. to 6 p.m. March 27, the symposium is spearheaded by the office’s Alternative Energy and Transportation Coordinator Ben Gouffon. His vision for the event is simple: at the intersection of human-accelerated climate destabilization and a revitalization of the collapsing biosphere sits every individual and their actions. His hope is that this symposium is an avenue for every attendee to discover what they can do for Knoxville, the university and the planet they call home.
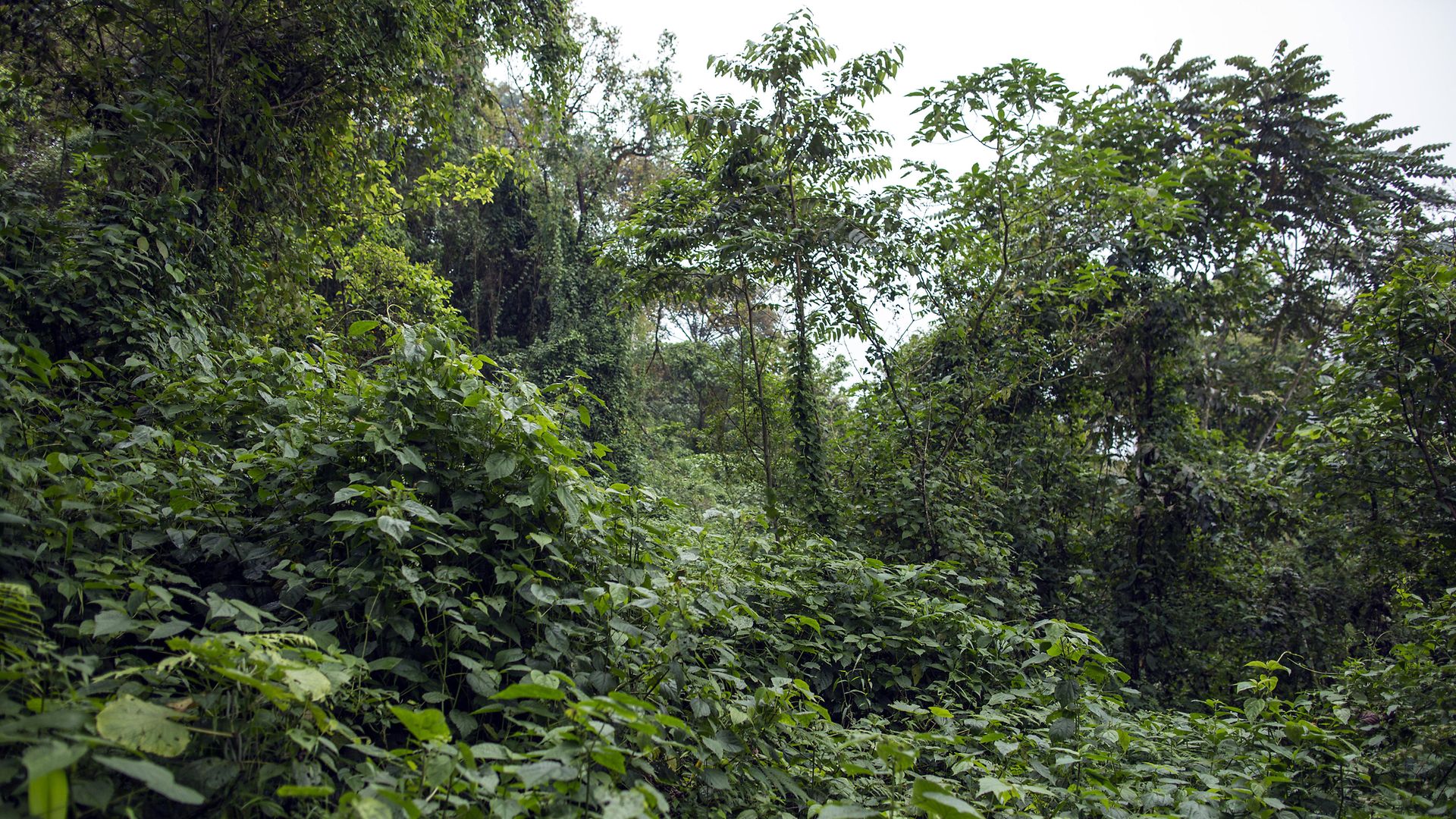 Cameroon’s vast and species-rich rainforests are of great importance for global biodiversity and the climate. They are also an important source of food and income for local people. A new study on hunting patterns in the jungles of West Africa includes research gathered by a University of Tennessee professor. Thomas Imo/German Federal Government
Cameroon’s vast and species-rich rainforests are of great importance for global biodiversity and the climate. They are also an important source of food and income for local people. A new study on hunting patterns in the jungles of West Africa includes research gathered by a University of Tennessee professor. Thomas Imo/German Federal Government
Adam Willcox subsisted on bush meat during African hunting study
Katie Donaldson is a communications specialist for the University of Tennessee School of Natural Resources.
KNOXVILLE — Data collected by a University of Tennessee research associate nearly 30 years ago is part of an extensive study that focuses on hunting patterns in African tropical forests.
Adam Willcox, a research associate professor in the UT Institute of Agriculture School of Natural Resources, co-authored the article, which was published recently in Nature Sustainability. “Regional patterns of wild animal hunting in African tropical forests” was also written by Daniel J. Ingram, research fellow at the University of Kent, and several other researchers. The data show how hunting management is needed to sustain wild animal populations in West and Central Africa.
The article uses data collected from 1991 to 2022 in 83 different studies to create a regional analysis of hunting patterns. Willcox contributed to the publication using research and data he gathered from 1996 to 2001 while promoting agroforestry in the U.S. Peace Corps in Cameroon. “I was in a lowland tropical forest. We did not have domestic alternatives for protein. We had to eat wild animals,” Willcox said. “My research followed 100 hunters around a wildlife sanctuary in Cameroon and their harvests.”
- university of tennessee professor ate research subjects
- adam willcox
- ut institute of agriculture
- human hunting patterns
- bush meat
- hunting management
- ut ag research
- nature sustainability
- wild animal populations in west and central africa
- biodiversity
- subsistence hunting
- agroforestry
- university of kent
Editorial: Old paradigms persist in proposed development of urban forest at UNC Asheville
Written by Noah Poulos UNC Asheville seems poised to develop a 45-acre forested tract in North Asheville into university amenities and housing. A grassroots movement has emerged to fight the proposal, such as Save the Woods, which has 3,000 members on Facebook. Save the Woods via social media
UNC Asheville seems poised to develop a 45-acre forested tract in North Asheville into university amenities and housing. A grassroots movement has emerged to fight the proposal, such as Save the Woods, which has 3,000 members on Facebook. Save the Woods via social media
The university indicates development of 45-acre wooded property is pending as community rallies
Noah Poulos is a farmer, writer, educator and UNC Asheville graduate who lives in Western North Carolina.
ASHEVILLE — Many have come to know a small forest in North Asheville as an extension of their home.
In these humble woods of the Experimental Forest, near a botanical park and U.S. Forest Service research station, pileated woodpeckers peck vigorously in the canopy. Towering pines dapple the light on the forest floor as day turns to dusk.
It is a place that has become a mainstay of this community and people are deeply connected to it — through stories, memories, relationships and a deep appreciation for what a small woodland can offer.
This forest, while open to the public, is owned by UNC Asheville, which recently shared plans to develop it for additional campus amenities.
Opposition has arisen to the university’s development plans, especially since a statement from the institution that strongly implies development will proceed as part of an overall expansion and revenue plan.
Industry-backed legislation would bar the science behind hundreds of environmental protections
Written by Sharon Lerner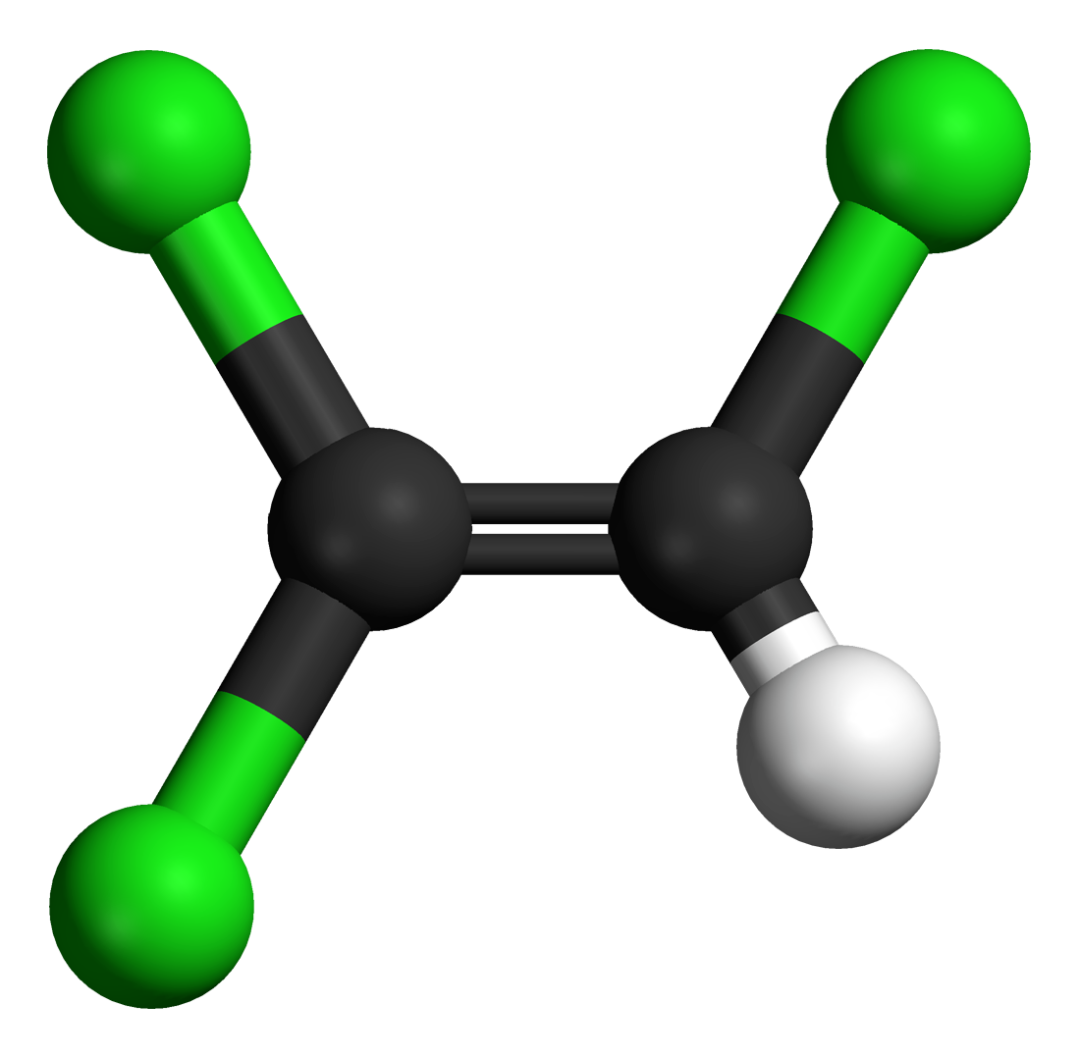 Trichloroethylene is among the chemicals deemed a serious public health risk by way of the Environmental Protection Agency’s IRIS database. Legislation in Congress could bar the use of IRIS and its associated scientific methods from being used to calculate the environmental and human health risks of chemicals such as TCE, a proven carcinogen. ChemLibrarian/Wikipedia Commons
Trichloroethylene is among the chemicals deemed a serious public health risk by way of the Environmental Protection Agency’s IRIS database. Legislation in Congress could bar the use of IRIS and its associated scientific methods from being used to calculate the environmental and human health risks of chemicals such as TCE, a proven carcinogen. ChemLibrarian/Wikipedia Commons
Two bills in Congress would prohibit the Environmental Protection Agency from using hundreds of chemical assessments completed by its IRIS program in environmental regulations or enforcement.
This story was originally published by ProPublica.
WASHINGTON, D.C. — For decades, Republican lawmakers and industry lobbyists have tried to chip away at the small program in the Environmental Protection Agency that measures the threat of toxic chemicals.
Most people don’t know IRIS, as the program is called, but it is the scientific engine of the agency that protects human health and the environment. Its scientists assess the toxicity of chemicals, estimating the amount of each that triggers cancer and other health effects. And these values serve as the independent, nonpartisan basis for the rules, regulations and permits that limit our exposure to toxic chemicals.
Now IRIS faces the gravest threat to its existence since it was created under President Ronald Reagan four decades ago.
Legislation introduced in Congress would prohibit the EPA from using any of IRIS’ hundreds of chemical assessments in environmental rules, regulations, enforcement actions and permits that limit the amount of pollution allowed into air and water. The EPA would also be forbidden from using them to map the health risks from toxic chemicals. The bills, filed in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives earlier this year, are championed by companies that make and use chemicals, along with industry groups that have long opposed environmental rules. If it becomes law, the “No IRIS Act,” as it’s called, would essentially bar the agency from carrying out its mission, experts told ProPublica.
“They’re trying to undermine the foundations for doing any kind of regulation,” said William Boyd, a professor at UCLA School of Law who specializes in environmental law. Boyd noted that IRIS reports on chemicals’ toxicity are the first step in the long process of creating legal protections from toxic pollutants in air and water.
“If you get rid of step one, you’re totally in the dark,” he said.
If the act passes, companies could even use the law to fight the enforcement of environmental rules that have long been on the books or permits that limit their toxic emissions, environmental lawyers said.
- iris
- propublica
- chemical regulation
- chemical pollution epa
- chemical database
- no iris act
- sharon lerner
- tce
- epa chemical regulations
- trump and environment
- environmental regulations
- carcinogens
- public health protection
- worst chemicals
- forever chemicals
- propublic environment
- propublica environment reporting
- best environmental reporting
- integrated risk information system
- toxic pollution
- environmental protection agency
More...
Butterflies decline by 20 percent since 2000 due in large part to pesticide use
Written by Eliza Grames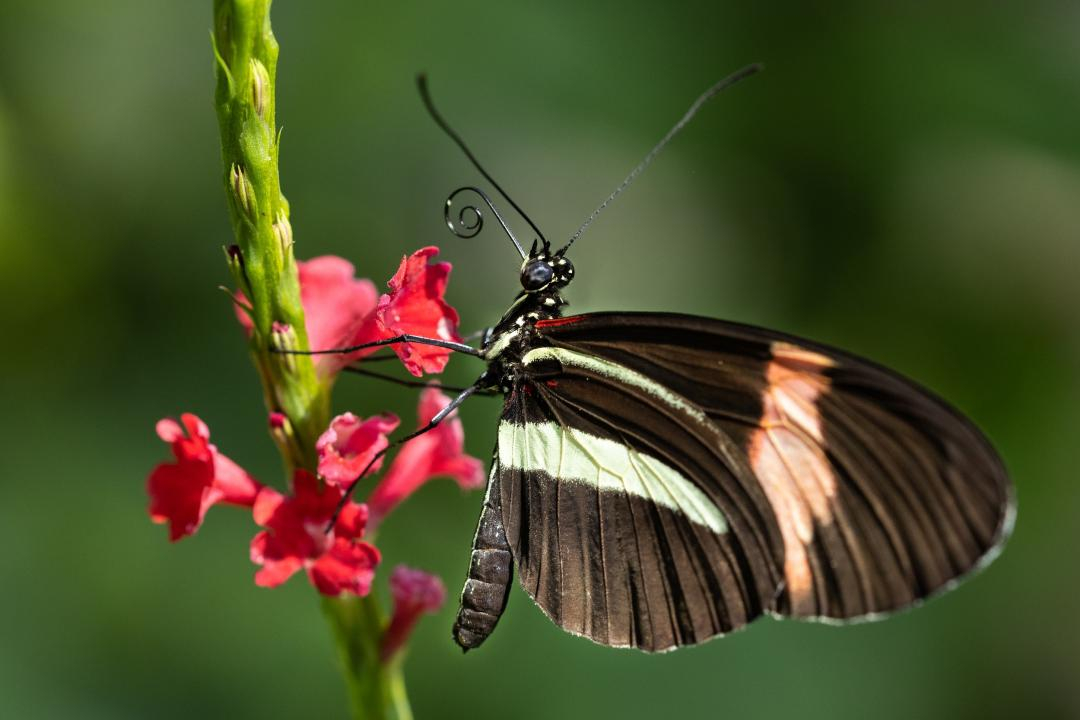 A postman butterfly feeds on a bloom in the Tennessee Aquarium’s Butterfly Garden in Chattanooga. At any one time, the garden may host 1,000 to 1,500 butterflies representing more than 200 species. Courtesy Tennessee Aquarium
A postman butterfly feeds on a bloom in the Tennessee Aquarium’s Butterfly Garden in Chattanooga. At any one time, the garden may host 1,000 to 1,500 butterflies representing more than 200 species. Courtesy Tennessee Aquarium
A third of species declined by half in U.S.; relatively simple steps can improve outlook
This story was originally published by The Conversation.
If the joy of seeing butterflies seems increasingly rare these days, it isn’t your imagination.
From 2000 to 2020, the number of butterflies fell by 22% across the continental United States. That’s 1 in 5 butterflies lost. The findings are from an analysis just published in the journal Science by the U.S. Geological Survey’s Powell Center Status of Butterflies of the United States Working Group, which I am involved in.
We found declines in just about every region of the continental U.S. and across almost all butterfly species.
Overall, nearly one-third of the 342 butterfly species we were able to study declined by more than half. Twenty-two species fell by more than 90 percent. Only nine actually increased in numbers.
Some species’ numbers are dropping faster than others. The West Coast lady, a fairly widespread species across the western U.S., dropped by 80 percent in 20 years. Given everything we know about its biology, it should be doing fine — it has a wide range and feeds on a variety of plants. Yet its numbers are absolutely tanking across its range.
Updated 4/18: Smoky gray: Former Smokies leader warns of more funding cuts; popular campsites remain closed; still little information on cuts at Great Smoky Mountains National Park
Written by Elan Young, Ben Pounds and Thomas Fraser Campers are seen enjoying a morning at Elkmont Campground in Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Elkmont is one of the Smokies campgrounds still open. National Park Service
Campers are seen enjoying a morning at Elkmont Campground in Great Smoky Mountains National Park. Elkmont is one of the Smokies campgrounds still open. National Park Service
National parks advocate and former Smokies official warns of funding shortfalls as closures continue, concerns persist, and people resist
KNOXVILLE — Funding for national parks has never amounted to much, and the federal government will cut even more if people don’t speak out in defense of the country’s natural and ecological crown jewels.
That was the message from Phil Francis, chairman of the Coalition to Protect American National Parks and former acting superintendent of Great Smoky Mountains National Park. He spoke to an audience at Knoxville’s Schulz Bräu Brewing Company hosted by Discover Life in America. Francis said that due to rising concerns his organization grew from 500 members to over 4,000 during the Trump administration. The coalition, he said, includes many people like himself who used to work for the park system, including the former superintendent of Acadia National Park.
Francis advocated that others should lobby government officials to continue to support the parks.
“If you don’t speak up, it makes it a lot more difficult,” he told the audience.
- elan young
- smokies job cuts
- federal job cuts
- rangers
- smokies rangers fired
- how many lost jobs at smokies
- smokies parking fees
- great smoky mountains economic impact
- national parks conservation association
- association of national park rangers
- hellbender press reporting on job cuts
- probationary workers fired
- great smoky mountains national park
- big south fork national river and recreation area
- maintenance backlog
- jeff hunter
- bill wade
- cades cove loop road
- carfree experience in cades cove
- carfree wednesdays in cades cove
- garry shores
- townsend
- townsend protest
- gatlinburg protest
- phil francis
- discover life in america
- ben pounds
- national park funding
- trump national park cuts
 Debris hangs from trees on the banks of the French Broad River near the main building of Hot Springs Resort and Spa. The river gauge at Hot Springs was offline during the main rain events immediately preceding the Sept. 27, 2024 floods but registered a peak just under 21 feet. The record stage is 22 feet, but that record will likely fall after review of provisional weather-gauge data by the National Weather Service. Much of the debris generated by flooding on the French Broad River in Western North Carolina made its way downstream toward Douglas Lake in Tennessee. Thomas Fraser/Hellbender Press
Debris hangs from trees on the banks of the French Broad River near the main building of Hot Springs Resort and Spa. The river gauge at Hot Springs was offline during the main rain events immediately preceding the Sept. 27, 2024 floods but registered a peak just under 21 feet. The record stage is 22 feet, but that record will likely fall after review of provisional weather-gauge data by the National Weather Service. Much of the debris generated by flooding on the French Broad River in Western North Carolina made its way downstream toward Douglas Lake in Tennessee. Thomas Fraser/Hellbender Press
Volunteers needed for 36th Ijams River Rescue set for March 8
KNOXVILLE — The thousand-year rains brought by Hurricane Helene flushed incalculable amounts of garbage from multiple major watersheds in East Tennessee and Western North Carolina in late September 2024. The Tennessee Wildlife Resources Agency and Tennessee Valley Authority, for instance, resorted to booms and cranes to corral and collect thousands of tons of garbage along more than 200 miles of Douglas Lake shoreline. The cleanup continues.
High water downstream also carried debris and detritus of every description into Knox County via the French Broad River, which then deposited it along urban and regional lake and stream banks.
Removing this pulse of pollution and flotsam from the Tennessee River, already known as a conduit of microplastics, could take years or generations. You can start the process March 8 along multiple TVA lakes in the area. We all live downstream.
Here’s the release from Ijams Nature Center, one of the main sponsors of the annual event:
Volunteer and make your community a cleaner, healthier place to live, work and play during the 36th annual Ijams River Rescue from 10 a.m. to 1 p.m. Saturday, March 8. A severe weather date is set for Saturday, March 15.
Ijams Nature Center’s annual cleanup event brings together hundreds of individuals, families, Scout troops, businesses and church groups to remove tons of trash and tires from sites along the Tennessee River, creeks and streams. Sites are typically located in Knox, Anderson and Blount counties.
Updated 2/28: Energy secretary on visit to an uncertain Oak Ridge shrugs at climate change; offers little concrete update on federal cuts
Written by Ben PoundsU.S. Sen. Bill Hagerty, R-Tenn.; U.S. Secretary of Energy Chris Wright; Rep. Chuck Fleischmann; R-Chattanooga; and Open AI CEO Greg Brockman spoke with the press during a tour of Oak Ridge-area nuclear facilities. Ben Pounds/Hellbender Press
Visit by energy secretary doesn’t address program cuts as former fracking CEO downplays climate change threat; visit comes following diversity program cuts; full extent of Oak Ridge impacts still unknown
Hellbender Press typically avoids the use of anonymous sources. The sources in this story spoke on condition they not be identified so they could speak on a sensitive matter.
This story will be updated. The original stories continue below.
OAK RIDGE — U.S. Secretary of Energy Chris Wright denied that climate change was a “crisis” and downplayed its threat during a visit to an international hub of scientific expertise rattled by early actions of the second Trump Administration. His visit did little to allay fears of cuts to staff and programs at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, where the most concrete signs of change have been the dismantling of diversity efforts.
Wright visited ORNL on Feb. 28, and at a press conference defended the Trump administration’s actions on climate change, energy sources and the Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), a group headed by Elon Musk that has recommended cutting programs and staff in various government departments.
He did not announce any layoffs at the lab itself, however, and implied research related to climate there will continue. Oak Ridge National Laboratory is home to many kinds of related research, including at the Climate Change Science Institute. CCSI does modeling and gathers data on the climate, as well as working on solutions to the problem.
Wright promoted research on artificial intelligence, which he called “Manhattan Project II,” and nuclear energy, and he appeared alongside Sen. Bill Hagerty, R-Tenn., Rep. Chuck Fleischmann R-Chattanooga and Open AI CEO Greg Brockman, who also spoke and answered questions.
“I don’t think you’ll see any reduction in the science that we do regarding climate change or any of these other really big questions,” said Wright in response to a reporter’s questions about how cuts at the lab might affect climate change-related research at ORNL, which his department funds through a partnership with contractor Battelle and the University of Tennessee. He said, however, he still “100 percent” believed there was no climate “crisis” and said scientific reports backed up his view.
“We haven’t seen an increase in the frequency or intensity of hurricanes, floods, droughts, storms. Wildfires are on an uptick because we stopped managing our forests,” he said. “Deaths from extreme weather, which is what you hear the press and politicians’ fearmongering about, it declined over 90 percent in my lifetime as the population’s grown. So climate change is a real phenomenon. It’s just not even remotely close to the world’s biggest problem.” He also said an intergovernmental climate change report also showed economists saying climate change was not as important as issues like education, free trade and “empowerment.”
These claims are a mixed bag of truth. While the frequency of hurricanes hitting the United States, for example, hasn’t increased, a recent Columbia University study showed the tropical cyclones’ intensity for the East and Gulf Coasts has. Also unmentioned by Wright was any impact the climate has on disease or health conditions apart from extreme weather, a subject on which experts at Tennessee’s own Vanderbilt University have sounded the alarm.
Wright was CEO of a hydraulic fracking company, Liberty Energy, before his appointment.
“It’s a real thing, but nothing in the science of climate change or in the economics of climate change shows it to be the world’s biggest problem,” Wright said. “When you call something a crisis, it means we don’t have time to stop and think. We’ve just got to take action. That’s exactly the opposite of what climate science is.”
During the meeting, he also defended Musk, DOGE and Trump’s actions generally while not announcing any such cuts for the civilian research at Oak Ridge National Laboratory or the weapons maintenance at Y-12, which is managed by a different contractor. A reporter at the event mentioned an earlier instance in which workers at Y-12 National Security Complex received termination letters that were then rescinded. While the reporter asked him to offer reassurance on job security, he sidestepped that question.
- doge oak ridge
- doge cuts in oak ridge
- oak ridge national laboratory climate change institute
- did oak ridge get doge cuts
- trump and environment
- ornl jobs
- ornl employee meeting
- doe diversity
- doe office of science
- stephen streiffer
- inflation reduction act clean energy
- doe science focus
- ben pounds
- ornl source
- climate change
- is climate change real?
- chris wright
- energy secretary chris wright
- greg brockman
- open ai