
9 Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure (30)
Build resilient infrastructure, promote inclusive and sustainable industrialization and foster innovation
ORNL wants to leave watercraft carbon emissions in its wake
 This Caterpillar in-line 6-cylinder marine diesel engine will be the subject of research and development for efficient, more climate-friendly marine propulsion with methanol fuel. Genevieve Martin, ORNL/U.S. Dept. of Energy
This Caterpillar in-line 6-cylinder marine diesel engine will be the subject of research and development for efficient, more climate-friendly marine propulsion with methanol fuel. Genevieve Martin, ORNL/U.S. Dept. of Energy
OAK RIDGE — The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Caterpillar Inc. have entered into a cooperative research and development agreement to investigate methanol as an alternative fuel source for four-stroke internal combustion marine engines. The collaboration supports efforts to decarbonize the marine industry, a hard-to-electrify transportation sector.
As the U.S. continues to seek ways to reduce environmentally harmful greenhouse gas emissions, methanol is an attractive fuel alternative to diesel because it reduces carbon emissions. Methanol also reduces emissions of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. In addition, methanol’s relatively high energy density makes it easier to store on marine vessels than gaseous fuels meaning it can be more easily integrated into overall existing engine design and operation.
Greener solution powers new method for lithium-ion battery recycling
 ORNL researchers Lu Yu and Yaocai Bai examine vials that contain a chemical solution that causes the cobalt and lithium to separate from a spent battery, followed by a second stage when cobalt precipitates in the bottom. Carlos Jones/ORNL/DOE
ORNL researchers Lu Yu and Yaocai Bai examine vials that contain a chemical solution that causes the cobalt and lithium to separate from a spent battery, followed by a second stage when cobalt precipitates in the bottom. Carlos Jones/ORNL/DOE
OAK RIDGE — Used lithium-ion batteries from cell phones, laptops and a growing number of electric vehicles are piling up, but options for recycling them remain limited mostly to burning or chemically dissolving shredded batteries. The current state-of-the-art methods can pose environmental challenges and be difficult to make economical at the industrial scale.
The conventional process recovers few of the battery materials and relies on caustic, inorganic acids and hazardous chemicals that may introduce impurities. It also requires complicated separation and precipitation to recover the critical metals. However, recovering metals such as cobalt and lithium could reduce both pollution and reliance on foreign sources and choked supply chains.
This research is funded as a project of the Advanced Battery Recycling Consortium, or ReCell, a program of the Vehicle Technologies Office within DOE’s Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy. Lu Yu and Yaocai Bai and researchers Rachid Essehli and Anuj Bisht contributed to the study, which utilized the DOE’s Center for Nanophase Materials Science at ORNL.
— Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL separates rare earth from the chaff
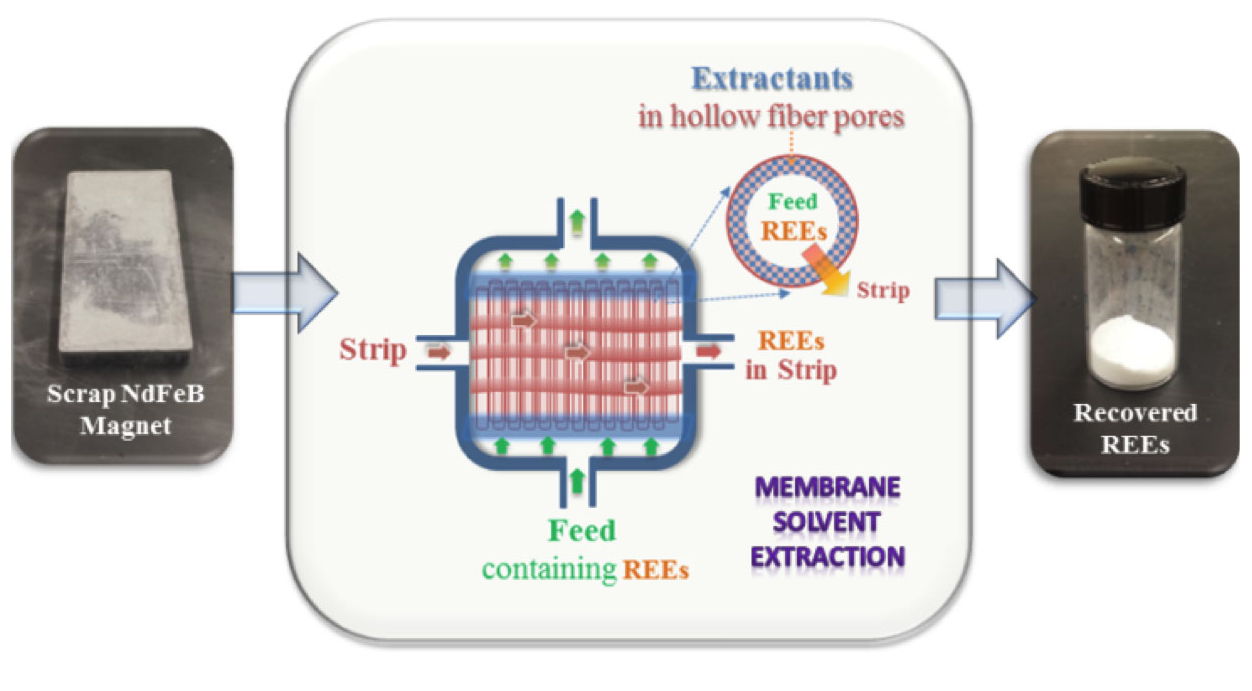 Membrane solvent extraction schematic. ORNL
Membrane solvent extraction schematic. ORNL
OAK RIDGE — Caldera Holding, the owner and developer of Missouri’s Pea Ridge iron mine, has entered a nonexclusive research and development licensing agreement with Oak Ridge National Laboratory to apply a membrane solvent extraction technique, or MSX, developed by ORNL researchers to process mined ores. MSX provides a scalable, efficient way to separate rare earth elements, or REEs, from mixed mineral ores.
The MSX technology was pioneered at ORNL by researchers in the Department of Energy’s Critical Materials Innovation Hub, or CMI, led by Ames National Laboratory. The inventors, Ramesh Bhave and Syed Islam of ORNL’s Chemical Sciences Division are named in 26 inventions and five active licenses related to the recovery of REEs.
TDEC releases money to help rubber meet the road
KNOXVILLE — The Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation granted $350,197 to the University of Tennessee from the Tire Environmental Act Program.
“We are seeing great advances in repurposing tires for environmental benefits,” said TDEC Deputy Commissioner Greg Young. ”Programs like this not only help clean up sites of used tires, they involve innovative new uses for them. We congratulate UT-Knoxville on this project.”
UTK is partnering with the Tennessee Department of Transportation (TDOT) to install a series of pavement test sections using the technologies developed from this project. Benefits of including rubber in asphalt pavement mixes include improved skid resistance, cracking resistance, and noise reduction.
The purpose of the Tire Environmental Act Program is to select and fund projects that best result in beneficial uses for waste tires. Projects must qualify for one of three categories: tire processing/recycling, tire-derived material use, or research and development. The program provides grant funding to eligible entities, including local governments, non-profit organizations, higher education institutions, K-12 schools and for-profit businesses.
Tennessee established the Tire Environmental Fund in 2015. Upon the first retail sale of a new motor vehicle to be titled and registered in Tennessee, a flat fee based on the number of a vehicle’s wheels is assessed. The fee goes into the fund, which is used for projects creating or supporting beneficial end uses for waste tires.
Since 2015, grantees have been awarded almost $6.8 million, and approximately 5.5 million tires or nearly 58,000 tons of scrap tires have been diverted from landfills. The tires are repurposed for use in rubberized asphalt, tire-derived aggregate, tire-derived fuel, granulated rubber porous flexible pavement, and other beneficial end uses that result in tires being diverted from landfills for a higher and better use.
— Tennessee Department of Environment and Conservation
Residential glass collection program to launch in November, as Knoxville startups tackle sustainability
Written by MaryBeth Mahne KnoxFill founder Dr. Michaela Barnett was recently featured on WUOT to address trash and sustainability. KnoxFill
KnoxFill founder Dr. Michaela Barnett was recently featured on WUOT to address trash and sustainability. KnoxFill
This article was originally published on WUOT in a collaboration with students from the University of Tennessee's Department of Journalism and Media
Two Knoxville-based startups are tackling the challenges of waste and sustainability, one household at a time
KnoxFill, founded by Dr. Michaela Barnett, is the city’s only refillery, and provides household and food products, ranging from shampoo and laundry detergent to coffee and tea.
Vitriform3D, a 3D printer technology focused on using glass waste and converting it into architectural building products, was founded by Alex Stiles, PhD and Dustin Gilmer, PhD.
Both businesses are filling a void left by a lack of state and local policies to address sustainability issues, and by the logistics challenges of recycling. “We know from the science that recycling can be part of a sustainable waste management program, but it really comes after trying to reduce source waste,” Barnett said. “Recycling really should be a last resort.”
Vitriform3D offers consumers the chance to recycle, and know that their recyclables are also being re-used. Knoxville has long lacked easy glass recycling capabilities; currently, residents have to transport their own glass to one of five repositories around the city. “We’re launching a service we call Fourth & Glass, Stiles said. “That is Knoxville’s first dedicated glass only recycling program. We do have the equipment to handle glass and turn it into new products.”
- knoxfill
- dr michaela barnett
- vitriform3d
- dustin gilmer
- alex stiles
- fourth & glass
- wuot
- glass recycling
- recycling in knoxville
- residential glass
- waste management
- knoxville
- extended producer responsibility
- single use plastic
- singlestream recycling
- glass processing
- 3d printing with glass
- waste management policy
Solar for All: An opportunity to expand alternative-energy access
Written by Southern Environmental Law Center The historic federal climate legislation known as the Inflation Reduction Act passed last summer. The $7 billion program will help fund rooftop solar projects benefiting communities with lower incomes and provide workforce development enabling millions of households’ access to affordable, resilient, and clean solar energy. Southern Environmental Law Center
The historic federal climate legislation known as the Inflation Reduction Act passed last summer. The $7 billion program will help fund rooftop solar projects benefiting communities with lower incomes and provide workforce development enabling millions of households’ access to affordable, resilient, and clean solar energy. Southern Environmental Law Center
A competitive grant program to bring solar power to people with limited incomes has found huge demand in the South
CHARLOTTESVILLE — Alabama, Georgia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Tennessee and Virginia, as well as other tribal governments, municipalities and nonprofits submitted applications for Solar for All, a new program designed to expand solar access.
Part of the historic federal climate legislation, the Inflation Reduction Act passed last summer, the $7 billion program will fund rooftop solar projects benefiting communities with lower incomes and provide workforce development enabling millions of households’ access to affordable, resilient and clean solar energy and related jobs. These funds have the potential to double the number of rooftop solar customers with 100 percent of cost saving solar, benefiting customers that would not otherwise be able to access solar.
“This is a generational opportunity to enable low-income households in the South to access affordable, resilient, and clean solar energy,” Thompson said.
Inflation Reduction Act charges positive clean-energy results in Southeast
 Electric car recharging. Courtesy Wikipedia Commons
Electric car recharging. Courtesy Wikipedia Commons
KNOXVILLE — This month marks the one-year anniversary of the Inflation Reduction Act, the most significant clean energy and climate action legislation in U.S. history, and our region is already seeing massive economic benefits. Consider this: just one year into the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), four Southeastern states rank in the top 10 nationally for new clean energy investments:
- Georgia: $18.83 billion with 22 new major clean energy projects, the 2nd most in the nation
- South Carolina: $11.71 billion with 20 new major clean energy projects,
the 3rd most in the nation - Tennessee: $5.76 billion with 13 new major clean energy projects, the 6th most in the nation
- North Carolina: $9.61 billion with 9 new major clean energy projects, the 10th most in the nation
- Florida: $503 million with 5 new major clean energy projects
The Southeast will also be a leading hub for electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing with more than 60,000 announced jobs, according to SACE's fourth annual Transportation Electrification in the Southeast report, produced with Atlas Public Policy, which will be published next Wednesday, September 6. The report also shows that Georgia leads all states in the country for announced EV manufacturing jobs. Join us for the webinar on September 6 at 11:00 a.m. ET to hear more highlights of the report.
While the economic growth numbers from the first year of the IRA are encouraging, the real impacts will be measured by the people and communities that will benefit from the transition to clean energy.
— Southern Alliance for Clean Energy
ORNL scientists are plugging big leaks in the plastics recycling stream
Written by Ben Pounds ORNL polymer scientists Tomonori Saito, left, and Sungjin Kim upcycled waste plastic to create a stronger, tougher, solvent-resistant material for new additive manufacturing applications. Ben Pounds/Hellbender Press
ORNL polymer scientists Tomonori Saito, left, and Sungjin Kim upcycled waste plastic to create a stronger, tougher, solvent-resistant material for new additive manufacturing applications. Ben Pounds/Hellbender Press
Thanks to an East Tennessee science powerhouse, recycling might become easier
This is the first in a series about ORNL’s Technology Innovation Program 2023
OAK RIDGE — Researchers at Oak Ridge National Laboratory developed a catalyst they say can break down a range of plastics, including polyesters, polycarbonates, polyurethanes and polyamides through a low-energy green process. In lay terms, the process can recycle many plastic-based carpets, ropes, other textiles, bottles, mattresses, protective equipment, car components and other things that weren’t previously easy to recycle into valuable chemicals.
Tomoronori Saito, a researcher at ORNL’s chemical sciences division presented some results of research at ORNL on July 14 as part of a symposium highlighting commercially valuable work that takes place at one of the country’s main science laboratories. Saito and fellow researcher Arif Arifuzzaman showed off plastics in varying levels of disintegration using their catalyst. It was part of the lab’s Technology Innovation Program 2023, promoting the lab’s research for possible business partnerships.
ORNL showcased its best science projects at July 14 tech conference

OAK RIDGE — Scientist-inventors from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory presented seven new technologies during the Technology Innovation Showcase on July 14 at the Joint Institute for Computational Sciences on ORNL’s campus.
The inventions are supported by ORNL’s Technology Innovation Program, or TIP, which provides targeted investments in new lab-developed technologies to enhance their commercial readiness. Since 2012, ORNL has invested more than $11 million in 49 projects, resulting in 37 commercial licenses and options with partners ranging from Fortune 100 companies to early-stage startups.
“ORNL’s researchers are creating next-generation technology for buildings, manufacturing, medicine and chemistry,” said Mike Paulus, ORNL Partnerships director. “The inventions selected for TIP investment show significant potential for commercialization.”
The showcase brings together inventors and commercialization professionals from ORNL with industry representatives for a morning of presentations followed by one-on-one meetings, tours and demonstrations.
![IMG 6085]() Caretaker Kody Hash leads a tour and points out cattle with tags at the UT AgResearch and Education Center’s Little River Animal and Environmental Unit. Ben Pounds/Hellbender Press
Caretaker Kody Hash leads a tour and points out cattle with tags at the UT AgResearch and Education Center’s Little River Animal and Environmental Unit. Ben Pounds/Hellbender Press
Computer-based milking methods offer the best cream of the crop
WALLAND — The University of Tennessee is using a new automated system to milk cows in the hope it’s easier on the animals than previous mechanized techniques.
It’s the newest feature of the UT AgResearch and Education Center’s Little River Animal and Environmental Unit at 3229 Ellejoy Road in Blount County.
As part of the unveiling of the equipment on May 2, visitors watched a cow on video walk through a ribbon to reach the new machines.
The milking machines, developed by Netherlands-based Lely Corporation, allow for cattle to walk up to the machines voluntarily to get special food in what a UT news release called a more “stress-free environment.”
More...
Udderly amazing: University of Tennessee to unveil robotic cow-milker
WALLAND — The University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture will host a demonstration of its new robotic milking technology at the UT AgResearch and Education Center’s Little River Unit in Blount County. The new system, developed by the Lely Corporation in the Netherlands, allows for the cows to be automatically milked at their own will in a stress-free environment. The demonstration is set for 10 a.m. May 2 and will include remarks from prominent university and community leaders.
The cows are trained to walk up to the robotic system, where each animal will be recognized by a sensor on its collar. The system then knows how much feed to give the cow while she’s being milked, based on historical data. The cow is free to eat, drink and rest while being milked, and in an area where there’s less cattle traffic. About 120 dairy cows can be milked and individual records kept through two robotic systems in a relatively short amount of time.
“The mission of UT AgResearch is to conduct leading-edge projects to serve the evolving needs of the agriculture and forestry industry in Tennessee and beyond,” said Hongwei Xin, dean of UT AgResearch.
“The introduction of milking robots into our existing traditional dairy production system at the Little River dairy facility allows our researchers to find answers to questions ranging from interactions between the animals and robots, impact on the animal’s production performance, and labor savings and profitability. The robotic milking system is part of the UT Precision Livestock Farming (PLF) initiative that aims to improve production efficiency and food supply chain robustness through enhanced animal welfare. UTIA is poised to be the leader in PLF in the region, the nation and the world.”
— University of Tennessee Institute of Agriculture
April 23 is new deadline of web survey: Advance Knox to hold ‘Priorities Week’ March 27 – April 6
Written by Wolf Naegeli
If you care about growth and transportation in Knox County, attend one of these meetings to share your ideas and express your opinions.
This article was updated on March 27 with first impressions from the March 27 meeting.
KNOXVILLE — Based on previous public input and data analysis, the Advance Knox project team has developed a list of proposed transportation projects that will accompany a future land use plan.
Advance Knox is an effort to define a vision and create a plan that will guide growth, land use, transportation, economic prosperity and quality of life in Knox County for years to come.
This is the first time the County has created an integrated land use and transportation plan, that is billed as having “the potential to be transformative.”
“Bringing land use and transportation components together is what will set this plan up for success,” said Knox County Mayor Glenn Jacobs. “Our teams are eager to hear community feedback and move toward adopting a final plan.”
Will this plan result in the transformation that you hope for?
Now is the time for you to check that it meets your needs, expectations and wishes. Or, to argue for better solutions by participating in this process.
Priorities Week is the third and final round of Advance Knox community outreach!
The electric-vehicle revolution brings environmental uncertainty at every turn
Written by Tim Lydon
As demand for electric vehicles soars, several roadblocks have emerged
This article was originally published by The Revelator.
Manufacturers, governments and consumers are lining up behind electric vehicles — with sales rising 60% in 2022, and at least 17 states are considering a California-style ban on gas cars in the years ahead. Scientists say the trend is a key part of driving down the transportation sector’s carbon emissions, which could fall by as much as 80% by 2050 under aggressive policies. But while EVs are cleaner than gas cars in the long run, they still carry environmental and human-rights baggage, especially associated with mining.
“If you want a lot of EVs, you need to get minerals out of the ground,” says Ian Lange, director of the Energy and Economics Program at the Colorado School of Mines.
Public comment: Environmental group leaders say TVA makes input difficult
Written by Dulce Torres Guzman Scott Banbury with the Tennessee Chapter of the Sierra Club said a handout provided at TVA’s Aug. 30 listening session stated recordings of the meeting were not allowed; a TVA spokesperson said recordings are, in fact, allowed. Flyer provided by Scott Banbury
Scott Banbury with the Tennessee Chapter of the Sierra Club said a handout provided at TVA’s Aug. 30 listening session stated recordings of the meeting were not allowed; a TVA spokesperson said recordings are, in fact, allowed. Flyer provided by Scott Banbury
Is TVA trying to gag its critics?
This story was originally published by Tennessee Lookout.
KNOXVILLE — While the Tennessee Valley Authority, a utility company that provides power to millions in Tennessee and other states, allows for public input into decisions, the process isn’t simple or transparent, say some regular attendees.
Take, for instance, a recent public listening session: representatives of the Tennessee Chapter of the Sierra Club say they were told they could not record the session despite a spokesman for TVA saying the opposite.
According to TVA spokesperson Scott Brooks, attendees are always allowed to record public meetings, provided they don’t cause a disturbance, but minutes before the session, members of the Tennessee chapter of the Sierra Club were prohibited from doing so.

