Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL partnership in Chattanooga tests new method for protecting quantum internet
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory collaborated with commercial utility EPB and the University of Tennessee Chattanooga to develop and test the first transmission of an entangled quantum signal using multiple wavelength channels and automatic polarization stabilization over a commercial network with no downtime. Morgan Manning/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
Oak Ridge National Laboratory collaborated with commercial utility EPB and the University of Tennessee Chattanooga to develop and test the first transmission of an entangled quantum signal using multiple wavelength channels and automatic polarization stabilization over a commercial network with no downtime. Morgan Manning/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
OAK RIDGE — Researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory joined forces with EPB of Chattanooga and the University of Tennessee at Chattanooga to demonstrate the first transmission of an entangled quantum signal using multiple wavelength channels and automatic polarization stabilization over a commercial network with no downtime.
The successful trial of this innovation marks another step toward the eventual creation of a quantum internet that could prove to be more capable and secure than existing networks.
Quantum computing relies on quantum bits, or qubits, to store information. Qubits, unlike the binary bits used in classical computing, can exist in more than one state simultaneously via quantum superposition, which allows combinations of physical values to be encoded on a single object.
The demonstration used automatic polarization compensation, or APC, to stabilize the polarization, or direction of the electric field oscillation in a light wave, of a signal sent over the EPB’s fiber-optic commercial quantum network. The approach used reference signals generated by lasers to continuously check the transmitted polarization, detected with an ultrasensitive method known as heterodyne detection.
APCs reduce data interference caused by outside forces like wind and temperature changes that can affect the fiber optic cables used to transmit quantum signals.
“One of our goals all along has been to develop quantum communications systems that operate seamlessly for users,” said Joseph Chapman, an ORNL quantum research scientist who led the study. “This is the first demonstration of this method, which enabled relatively fast stabilization while preserving the quantum signals, all with 100 percent uptime — meaning the people at either end of this transmission won’t notice any interruption in the signal and don’t need to coordinate scheduled downtime.”
The method enabled continuous transmission of the signals with no interruptions for more than 30 hours between the node on the University of Tennessee Chattanooga campus and two other EPB quantum network nodes, each about half a mile away. The UTC node held an entangled-photon source developed by Muneer Alshowkan, an ORNL quantum research scientist.
 The quantum network technology using automatic polarization compensation developed by ORNL was demonstrated in Chattanooga, Tennessee. The test utilized EPB’s fiber-optic commercial quantum network and involved the University of Tennessee Chattanooga and industry partner Qubitekk. Joe Chapman, Morgan Manning/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
The quantum network technology using automatic polarization compensation developed by ORNL was demonstrated in Chattanooga, Tennessee. The test utilized EPB’s fiber-optic commercial quantum network and involved the University of Tennessee Chattanooga and industry partner Qubitekk. Joe Chapman, Morgan Manning/ORNL, U.S. Dept. of Energy
ORNL engineering eco-friendly solvents
 ORNL researchers are using artificial intelligence to speed the identification of environmentally friendly solvents for industrial applications. Andy Sproles/ORNL, U.S. Department of Energy
ORNL researchers are using artificial intelligence to speed the identification of environmentally friendly solvents for industrial applications. Andy Sproles/ORNL, U.S. Department of Energy
OAK RIDGE — Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists developed a method leveraging artificial intelligence to accelerate the identification of environmentally friendly solvents for industrial carbon capture, biomass processing, rechargeable batteries and other applications.
The research targets a class of solvents known for being nontoxic, biodegradable, highly stable, cost-effective and reusable.
The scientists developed a method to predict solvent viscosity — a key property impacting performance for industrial applications. They compiled nearly 5,000 data points on 672 solvents, evaluated quantum chemical features that guide solvent molecular interactions, and deployed an algorithm called categorical boosting to quickly parse the data and determine the best candidates.
“We reduced computational time and complexity with our approach, while still incorporating all possible molecular interactions,” said ORNL’s Mohan Mood.
ORNL’s Michelle Kidder said, “Interpretable machine learning helps us to design solvents with desired properties for carbon capture by reducing experimental time and cost in the laboratory.”
Less carbon, more chill: ORNL tech reduces refrigerator CO2 emissions by 30 percent
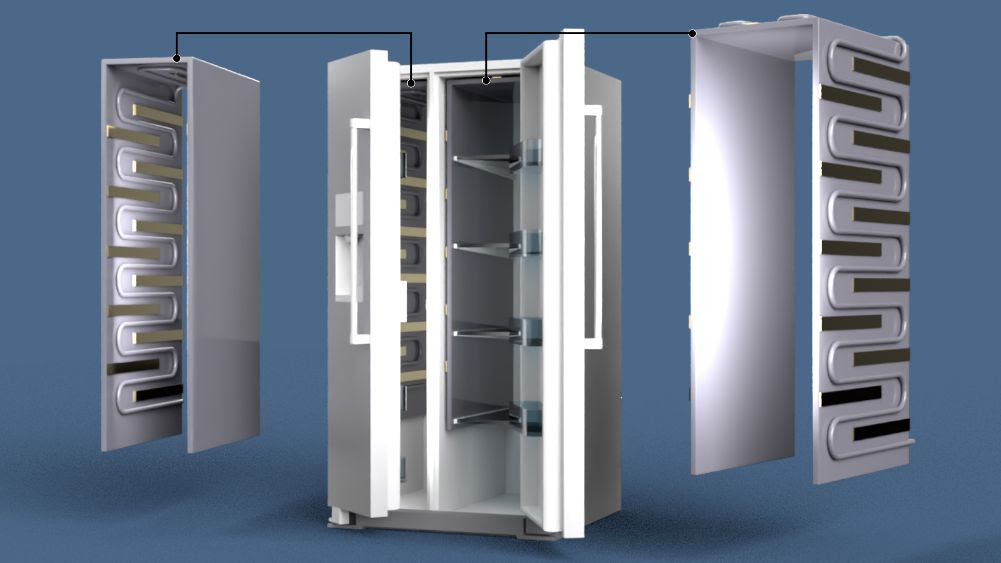 A novel technology developed by ORNL keeps food and beverages refrigerated with an advanced evaporator, phase change materials, metal foam, direct-contact defrosting technology and a low global warming refrigerant. Oak Ridge National Laboratory
A novel technology developed by ORNL keeps food and beverages refrigerated with an advanced evaporator, phase change materials, metal foam, direct-contact defrosting technology and a low global warming refrigerant. Oak Ridge National Laboratory
OAK RIDGE — A technology developed by Oak Ridge National Laboratory keeps food refrigerated with phase-change materials, or PCMs, while reducing carbon emissions by 30 percent.
More than 100 million household refrigerators in operation across the United States consume up to 2 kilowatts of electricity daily. These refrigerators contribute to energy consumption and carbon emissions by using compressors that cycle on and off day and night, pumping refrigerants across evaporator coils to maintain low temperatures for fresh and frozen compartments.
(Hellbender Press previously reported on the development of new coolants and systems at ORNL).
ORNL’s innovation uses advanced evaporators with PCMs installed in each compartment for cold energy storage. PCMs are useful for heating and cooling because they store and release energy when changing from solids to liquids or vice versa. Researchers applied porous metals, direct-contact defrosting technology and a refrigerant with low-global-warming potential to enhance performance and minimize environmental impact.
“PCMs are integrated with evaporator coils to keep temperature constant, requiring one operating cycle and allowing refrigerators to operate almost 100% at nighttime, when energy use is lower,” ORNL’s Zhiming Gao said. “This reduces electricity demand, saves costs and maintains efficiency.”
— Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL chemists invent a more efficient way to extract lithium
 Oak Ridge National Laboratory
Oak Ridge National Laboratory
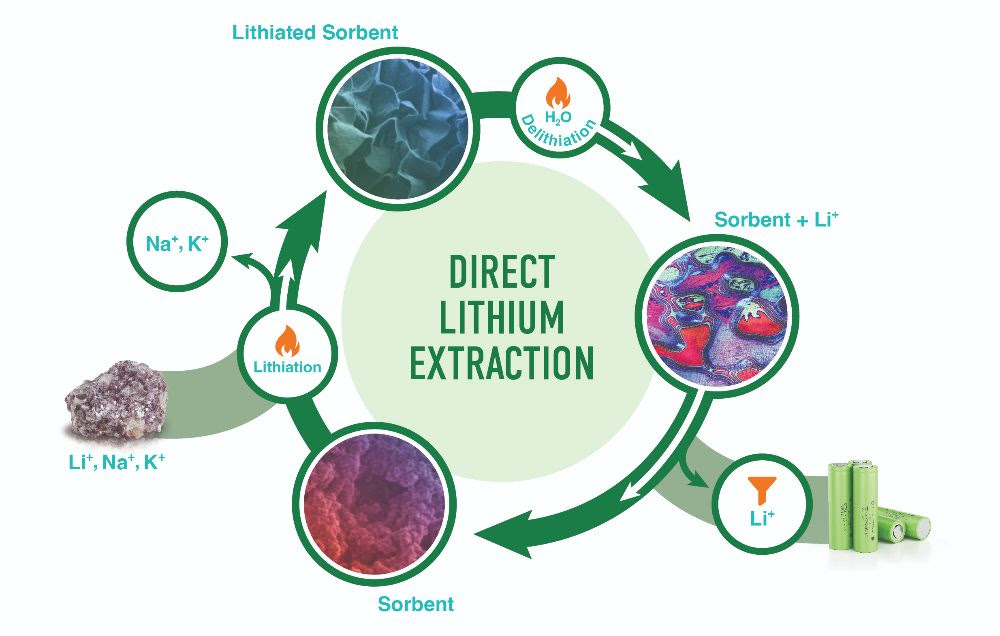
OAK RIDGE — Chemists at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory have invented a more efficient way to extract lithium from waste liquids leached from mining sites, oil fields and used batteries. They demonstrated that a common mineral can adsorb at least five times more lithium than can be collected using previously developed adsorbent materials.
“It’s a low-cost, high-lithium-uptake process,” said Parans Paranthaman, an ORNL Corporate Fellow and National Academy of Inventors Fellow with 58 issued patents. He led the proof-of-concept experiment with Jayanthi Kumar, an ORNL materials chemist with expertise in the design, synthesis and characterization of layered materials.
“The key advantage is that it works in a wider pH range of 5 to 11 compared to other direct lithium extraction methods,” Paranthaman said. The acid-free extraction process takes place at 140 degrees Celsius, compared to traditional methods that roast mined minerals at 250 degrees Celsius with acid or 800 to 1,000 degrees Celsius without acid.
Lithium is a lightweight metal commonly used in energy-dense and rechargeable batteries. Electric vehicles, which are needed to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050, rely on lithium-ion batteries. Industrially, lithium is extracted from brines, rocks and clays. The ORNL innovation may help meet rising demand for lithium by making domestic sources commercially viable.
ORNL wants to leave watercraft carbon emissions in its wake
 This Caterpillar in-line 6-cylinder marine diesel engine will be the subject of research and development for efficient, more climate-friendly marine propulsion with methanol fuel. Genevieve Martin, ORNL/U.S. Dept. of Energy
This Caterpillar in-line 6-cylinder marine diesel engine will be the subject of research and development for efficient, more climate-friendly marine propulsion with methanol fuel. Genevieve Martin, ORNL/U.S. Dept. of Energy
OAK RIDGE — The Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Caterpillar Inc. have entered into a cooperative research and development agreement to investigate methanol as an alternative fuel source for four-stroke internal combustion marine engines. The collaboration supports efforts to decarbonize the marine industry, a hard-to-electrify transportation sector.
As the U.S. continues to seek ways to reduce environmentally harmful greenhouse gas emissions, methanol is an attractive fuel alternative to diesel because it reduces carbon emissions. Methanol also reduces emissions of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides. In addition, methanol’s relatively high energy density makes it easier to store on marine vessels than gaseous fuels meaning it can be more easily integrated into overall existing engine design and operation.
ORNL separates rare earth from the chaff
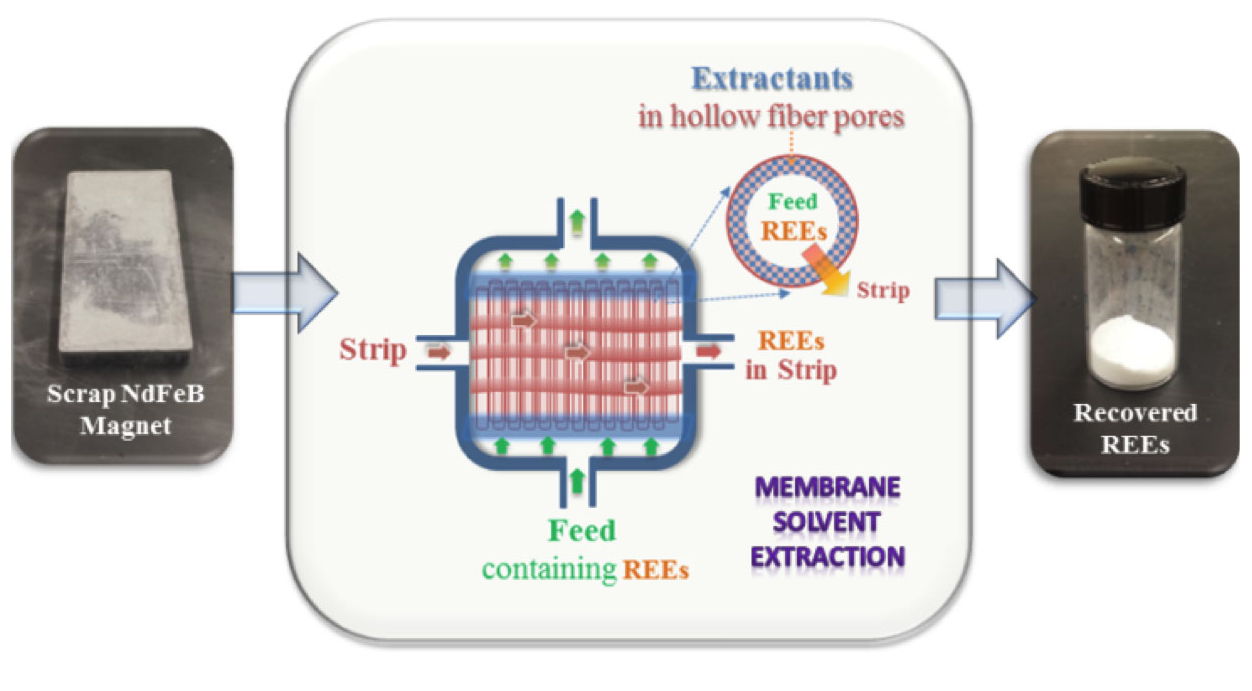 Membrane solvent extraction schematic. ORNL
Membrane solvent extraction schematic. ORNL
OAK RIDGE — Caldera Holding, the owner and developer of Missouri’s Pea Ridge iron mine, has entered a nonexclusive research and development licensing agreement with Oak Ridge National Laboratory to apply a membrane solvent extraction technique, or MSX, developed by ORNL researchers to process mined ores. MSX provides a scalable, efficient way to separate rare earth elements, or REEs, from mixed mineral ores.
The MSX technology was pioneered at ORNL by researchers in the Department of Energy’s Critical Materials Innovation Hub, or CMI, led by Ames National Laboratory. The inventors, Ramesh Bhave and Syed Islam of ORNL’s Chemical Sciences Division are named in 26 inventions and five active licenses related to the recovery of REEs.
Oak Ridge research suggests rough weather ahead
OAK RIDGE — Researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Northeastern University modeled how extreme conditions in a changing climate affect the land’s ability to absorb atmospheric carbon — a key process for mitigating human-caused emissions. They found that 88 percent of Earth’s regions could become carbon emitters by the end of the 21st century.
Climate extremes lasting months or years could reduce plant productivity, which governs Earth’s capacity to produce food, fiber and fuel. Events such as wildfires could generate bursts of emissions from carbon stored in forests.
The team used the open-source Community Earth System Model to simulate multiple variables, which enabled a holistic understanding of how climatic conditions interact.
“Our results suggest that meteorological extremes will become more frequent, intense and widespread due to the compound effect of high temperature, drought and fire,” said ORNL’s Bharat Sharma. “Tropical regions may face these to the most extreme degree.”
ORNL showcased its best science projects at July 14 tech conference

OAK RIDGE — Scientist-inventors from the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory presented seven new technologies during the Technology Innovation Showcase on July 14 at the Joint Institute for Computational Sciences on ORNL’s campus.
The inventions are supported by ORNL’s Technology Innovation Program, or TIP, which provides targeted investments in new lab-developed technologies to enhance their commercial readiness. Since 2012, ORNL has invested more than $11 million in 49 projects, resulting in 37 commercial licenses and options with partners ranging from Fortune 100 companies to early-stage startups.
“ORNL’s researchers are creating next-generation technology for buildings, manufacturing, medicine and chemistry,” said Mike Paulus, ORNL Partnerships director. “The inventions selected for TIP investment show significant potential for commercialization.”
The showcase brings together inventors and commercialization professionals from ORNL with industry representatives for a morning of presentations followed by one-on-one meetings, tours and demonstrations.